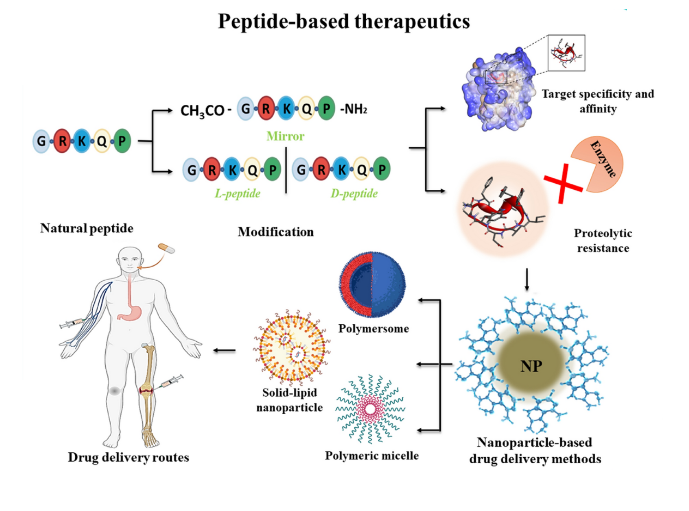
Introduction
Peptide-based therapies are emerging as a significant advancement in modern medicine, offering new hope for treating a wide range of diseases. These therapies use chains of amino acids (peptides) to mimic or influence natural biological processes in the body. From cancer treatments to managing metabolic disorders, peptide therapies are becoming a valuable tool in personalized medicine. This article will explore how peptide-based therapies work, their applications, benefits, and future potential in revolutionizing healthcare.
What are Peptide-Based Therapies?
Peptides are short chains of amino acids that are the building blocks of proteins. In the human body, peptides regulate various biological processes, including hormone production, immune responses, and cellular communication. Peptide-based therapies involve the use of synthetic or naturally derived peptides to treat diseases by interacting with specific receptors in the body to trigger desired biological responses.
These therapies are designed to be highly specific, meaning they can target particular cells or tissues, leading to more effective treatments with fewer side effects compared to traditional therapies.
Applications of Peptide-Based Therapies
- Cancer Treatment: Peptides are being explored for their ability to selectively target cancer cells. Peptide-based cancer therapies can deliver drugs directly to tumors, minimizing damage to healthy tissues. Additionally, certain peptides can enhance the body’s immune response to fight cancer cells more effectively, offering a promising approach to immunotherapy.
- Diabetes Management: Peptide-based drugs are already in use for managing diabetes. For example, GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) receptor agonists are used to regulate blood sugar levels by increasing insulin production. These therapies help patients with type 2 diabetes better control their glucose levels without the need for insulin injections.
- Antimicrobial Peptides: As antibiotic resistance becomes a growing concern, antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are being researched as a potential alternative. AMPs have broad-spectrum activity against bacteria, fungi, and viruses, making them a powerful tool in fighting infections that do not respond to conventional antibiotics.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Peptides can play a role in reducing blood pressure and preventing heart disease. Peptide-based drugs that mimic natural hormones are being used to treat conditions such as hypertension, heart failure, and atherosclerosis, improving patient outcomes.
- Weight Management: Some peptides, such as those that mimic appetite-suppressing hormones, are being used in weight management treatments. By regulating hunger signals, these therapies can help individuals manage their weight more effectively, reducing the risk of obesity-related diseases.
- Wound Healing: Peptides are being developed to accelerate wound healing by promoting the production of collagen and other proteins that are essential for tissue repair. This has potential applications in treating chronic wounds, such as diabetic ulcers.
Benefits of Peptide-Based Therapies
- High Specificity: Peptides are highly specific, allowing them to target particular cells or receptors in the body. This results in more effective treatments with fewer off-target effects compared to traditional drugs.
- Fewer Side Effects: Because peptides are naturally occurring in the body, peptide-based therapies are generally well-tolerated and have fewer side effects than many traditional medications.
- Personalized Medicine: Peptide therapies can be tailored to an individual’s unique biology, offering personalized treatment options that are more effective than one-size-fits-all approaches.
- Versatility: Peptides can be designed to target a wide range of diseases, from chronic conditions like diabetes and heart disease to acute infections and cancers. Their versatility makes them an attractive option for drug development.
Challenges in Peptide-Based Therapies
Despite their promise, peptide-based therapies face several challenges:
- Stability: Peptides can be broken down quickly in the body by enzymes, limiting their effectiveness. Researchers are working on ways to improve the stability of peptide drugs to ensure they remain active for longer periods.
- Cost: Manufacturing peptides can be expensive, which can drive up the cost of peptide-based therapies. However, advancements in peptide synthesis techniques may help reduce these costs in the future.
- Delivery Mechanisms: Ensuring that peptides are delivered to the right part of the body in the right amounts remains a challenge. Researchers are developing innovative drug delivery systems, such as nanoparticles and hydrogels, to improve the efficiency of peptide-based treatments.
The Future of Peptide-Based Therapies
The future of peptide-based therapies looks promising, with ongoing research and development expected to expand their use in various fields of medicine. Advances in peptide engineering, drug delivery systems, and personalized medicine are likely to unlock new possibilities for treating conditions that currently have limited treatment options.
Additionally, peptide vaccines are being explored for their potential in preventing diseases, including cancer and infectious diseases like COVID-19. These vaccines could offer long-lasting immunity with fewer side effects than traditional vaccines.
Conclusion
Peptide-based therapies represent a new frontier in medicine, offering targeted, effective treatments for a wide range of diseases. As research continues to advance, peptide therapies have the potential to revolutionize how we treat cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and more. With fewer side effects and greater specificity, peptide-based drugs are paving the way for more personalized and efficient healthcare solutions.
References:
- Craik, D. J., Fairlie, D. P., Liras, S., & Price, D. (2013). The future of peptide-based drugs. Chemical Biology & Drug Design.
- Otvos, L., & Wade, J. D. (2014). Current challenges in peptide-based drug discovery. Frontiers in Chemistry.
- Ramesh, S., & Gopinath, M. (2020). Peptide-based therapeutics: Current status and future directions. Journal of Clinical Medicine.